Table of contents
No headings in the article.
Meaning of Edge Computing
Edge computing is a distributed information technology (IT) architecture in which client data is processed at the periphery of the network, as close to the originating source as possible.Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the sources of data. This is expected to improve response times and save bandwidth. It is an architecture rather than a specific technology. It is a topology- and location-sensitive form of distributed computing.
How does Edge Computing Work
Edge computing is all a matter of location. In traditional enterprise computing, data is produced at a client endpoint, such as a user's computer. That data is moved across a WAN such as the internet, through the corporate LAN, where the data is stored and worked upon by an enterprise application. Results of that work are then conveyed back to the client endpoint.This remains a proven and time-tested approach to client-server computing for most typical business applications.
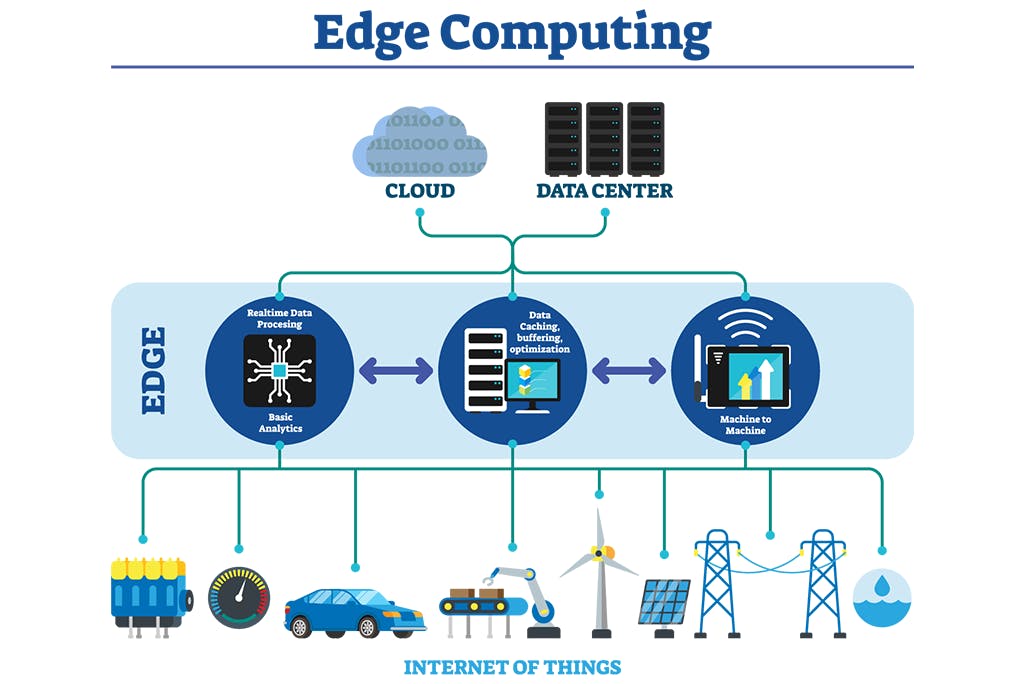
Advantages of Edge Computing
Security: While the emergence of IoT edge computing devices increases the networks' total attack vectors, it also offers some major safety benefits. The conventional cloud computing architecture is fundamentally centralized, which makes it extremely vulnerable to exploitation and power failures from decentralized denial of service (DDoS).
Speed: Edge computing's most significant advantage is the potential to improve network productivity by minimizing the latency. The data they accumulate does not have to move almost as far as it would under such a conventional cloud environment, since IoT edge computing devices manage private data or in neighboring edge data centers.
Performance Improvement: Edge computing also collects, analyzes, and conducts appropriate actions on the gathered data locally, in addition to collecting data for transfer to the cloud. Although these activities have been completed in milliseconds, no matter what all the operations might be, it is becoming important to optimize technical information.
Reducing Operational Costs: Communication, data management, throughput, and performance features are surprisingly costly in the cloud computing model. Edge computing, which has a substantially lower bandwidth demand and less bandwidth, remedies this inefficiency. A useful continuum from the computer to the cloud is produced through the implementation of edge computing, that can accommodate the vast amounts of data collected. Expensive bandwidth improvements are no longer needed, because gigabytes of data need not be transferred to the cloud.
Reliability: Related to security benefits gained by edge computing, this should not shock that it provides better performance. Through IoT edge computing systems and cloud network infrastructure located directly to end-users, there is less risk of a network issue in a faraway place impacting local customers. Even in the case of a local data center failure, since they perform critical processing capabilities wirelessly, IoT edge computing systems can continue to work efficiently on their own.